- solen.cz - Treatment according to McKenzie in the therapy of vertebrogenic disorders, MUDr. Marie TinkováNeurological Department of the Institute of Neurology, Prague
- pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - The effectiveness of McKenzie method compared to manual therapy for treating chronic low back pain
- bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com - The effectiveness of the McKenzie method in addition to first-line care for acute low back pain
McKenzie method as a help for back pain?
Back pain is one of the most common reasons for visiting a doctor or physiotherapist.
Article content
Back health problems are a very common cause of incapacity for work and early disability retirement. People resort to taking analgesics. The drugs provide short-term pain relief, but often do not address the real cause of the pain.
What is the purpose of the spine?
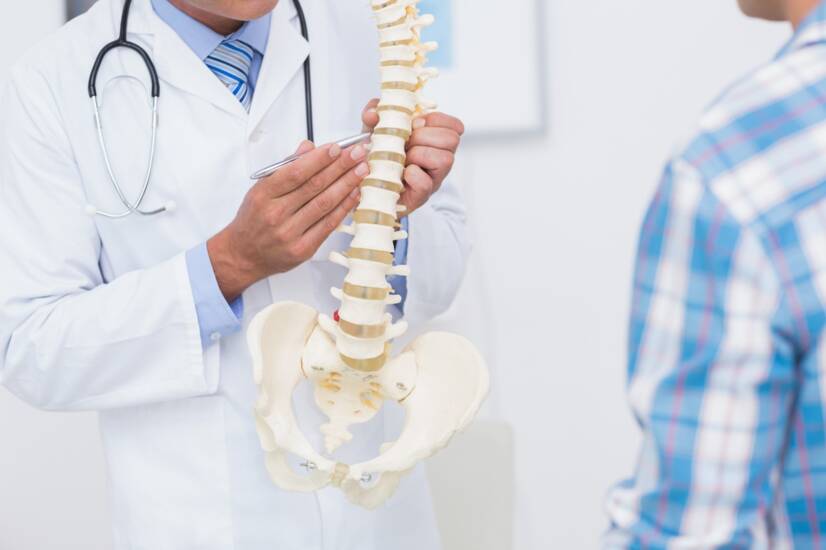
The human spine is an axial skeleton made up of 33-34 vertebrae, 23 soft intervertebral discs and surrounding stabilizing ligaments.
Together, they create space and protection for the spinal canal, from which nerve roots exit to the entire human body. Anatomically, the vertebrae of the spine are divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal segments.
The spine is a complex axial organ anatomically and functionally connected to the outermost structures and parts of the human body.
The spine is particularly important for:
- upright posture
- walking
- the position and movements of the head
- mobility of the trunk
- shock and pressure absorption
- chest stability
- correct breathing pattern
- weight transfer of body segments through the pelvis and lower limbs
Etiology of back pain
The etiology of low back pain is extensive.
It is related to age, genetic factors, complex medical history, degenerative processes, mechanical damage, lifestyle, work activity, exercise habits, physical activity and psychosocial factors of the individual.
Back pain can be experienced differently from different causes. Pain can be acute/chronic, dull/ sharp, muscular/nervous, deep/surface, easily or not easily localised.
The most common causes of back pain are:
- Poor posture
- Prolonged and incorrect sitting
- Lack of compensatory movement
- Imbalance of the musculoskeletal system
- Excessive stretching of the back
- Lifting heavy loads
- Sudden abrupt movement
- Injury or mechanical damage
- Degenerative changes in the vertebrae
- Disc displacement
- Disc herniation (herniated disc)
Treatment of back pain
Treatment of back pain depends on finding the cause of the pain using diagnostic procedures. These include a thorough history, facet examination (examination by sight), palpation (examination by touch), percussion examination (tapping) and specific physical methods (ultrasound, X-ray, CT scan, MRI, etc.).
Depending on the clinical findings, the degree of pain and mutual agreement with the patient, treatment is then determined. It can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment consists of non-invasive procedures such as physiotherapy, rehabilitation, specific movement exercises and restrictions, ergonomics in normal daily activities and the use of the beneficial effects of physical therapy (thermotherapy, hydrotherapy, electrotherapy, mechanotherapy and phototherapy).
As the spine is surrounded and stabilised by a number of muscle groups, it is important to correct the muscular imbalances that have arisen. It strengthens weakened muscles and, conversely, relaxes overworked muscles.
Modern treatment offers comprehensive physiotherapy methods focused on the back and specifically on intervertebral disc disorders.
The world's leading method in back pain therapy is the McKenzie Method.
McKenzie Method
The author of the method is the physiotherapist Robin McKenzie, who was born in New Zealand. During his student years he specialised in the diagnosis and treatment of back disorders with a focus on the intervertebral discs.
This internationally recognised method is also known as MDT - the Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy method.
McKenzie found that due to specific repetitive movements, the intervertebral disc gradually moves to its original location. Many years of practice and results have confirmed the effectiveness of his theory.
The principle of the McKenzie method
The main principle of the method is the concept of centralization (improvement) and peripheralization (deterioration).
Centralization is a phenomenon whereby the influence of therapy and repetitive movements results in improvement and retreat of pain from the periphery towards the center of the body.
This phenomenon is an indication that the therapy has been implemented well and that the exercises should be continued.
Conversely, the concept of peripheralisation is a phenomenon that increases the intensity of the pain and spreads it from the centre of the body to the periphery. This opposite phenomenon is a sign that the therapy should be discontinued and the direction of the movements performed should be changed.
The basic content of the method consists of 4 main steps:
- Examination
- Classification of the disorder
- Treatment management
- Prevention
1. Examination
The first step to successful treatment is a complete thorough examination by a trained MDT therapist. A personal consultation with the patient is necessary.
The examination starts from the very first moment of the meeting. The physiotherapist notices even the smallest details of the patient's musculoskeletal system.
The examination includes:
- interview with the patient
- taking a general medical history
- physiotherapy kinesiological analysis
- testing of specific postures and exercises
- training of specific movements
2. Classification of the disorder
After the examination, the diagnosis is evaluated and therapy is determined.
Robin McKenzie divides the causes of pain into 3 classification levels, called syndromes. Each level is characterised by specific phenomena, findings and a different type of pain.
He divides back disorders into postural syndrome, dysfunctional syndrome and derangement syndrome.
Postural syndrome is a disorder without structural tissue changes.
It is a functional problem in terms of incorrect posture, non-physiological spinal alignment and poor movement patterns leading to deformation of the soft structures of the body (muscles, ligaments, subcutaneous tissue).
The patient's dull pain usually occurs around the spine and does not progress from the body to the periphery.
Dysfunctional syndrome is characterized by poor postural and movement patterns that have caused some damage to the soft tissues.
There is shortening, stretching and weakening of muscle groups. This subsequently limits the patient's mobility. Pain is intense at the extremes of certain movements. It tends to subside when the movement is completed.
Derangement syndrome is a disorder syndrome that is often found in patients with back pain. It is characterised by structural tissue damage at the level of the vertebral segment of the spine.
It is primarily a structural change, narrowing, displacement or prolapse of the intervertebral disc. The pain is asymmetrical and may radiate to the periphery of the lower limbs. It is more intense with certain movements, standing up or prolonged sitting.
A neurological problem in the sense of irritation of a nerve emanating from the spinal canal may be part of the disorder.
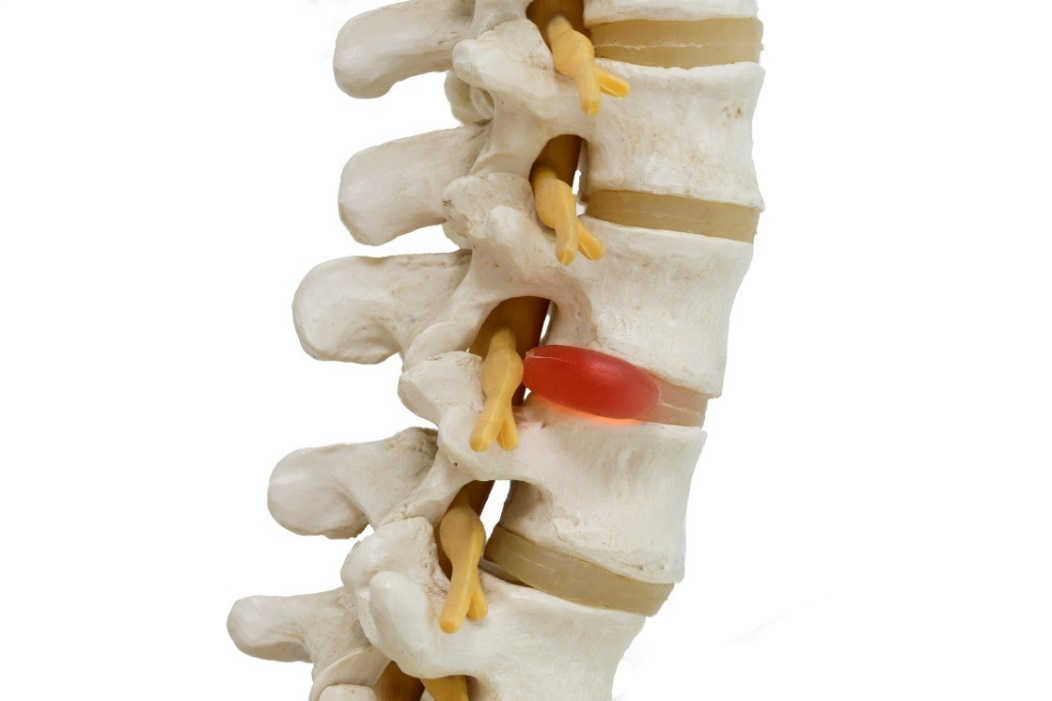
Nerve irritation
The intervertebral discs are softer elastic filling structures located between the vertebrae.
Their main function is stabilization, pressure and shock absorption, transmission of tensile forces and the ability to move the spine, such as bending and rotating the body.
Damage to the discs can take different forms and degrees of damage. The disc can be damaged, narrowed or displaced by degenerative and mechanical influences.
More severe damage is disc herniation, where the disc is displaced beyond the vertebral margins.
In addition to the displacement itself, the nerves that exit the spinal canal may be compressed. The person may experience neurological discomfort, such as tingling pain shooting to the periphery of the body, outside the damaged area of the spine.
Read more:
What is radiculopathy, radicular or root syndrome?
3. Treatment management
Based on the examination and classification of the syndrome, the actual therapy and management of the treatment occurs.
The MDT-trained therapist will thoroughly explain the selected exercises to the patient, demonstrate them and teach the patient how to perform them correctly. He/she will introduce the patient to the aids that are appropriate to facilitate the exercises and improve the effect of the therapy.
The basis of the treatment is simple and precise movements, which the patient repeats 5 times a day in the home environment.
Sessions with the therapist are required at the beginning of therapy. The aim is to minimise visits to the outpatient clinic. Robin McKenzie has tried to devise a method of treatment that is functional, simple and inexpensive for the patient.
What are the exact indications and contraindications for this worldwide method?
Indications of the McKenzie method
- Muscular imbalances of the musculoskeletal system
- Weakened/strained muscles
- Vertebrogenic algic syndrome
- Scoliotic posture and scoliosis
- Rheumatic pain
- Myalgia and neuralgia
- Sciatic nerve inflammation
- Nerve root irritation
- Hand or foot pain
- Displacement and dislocation of the intervertebral disc
- Disc herniation (herniated disc)
Contraindications to the McKenzie method
- Cancer in the spine
- Malignant tumour
- Instability of the bony structures of the spine
- Inflammatory disease in the acute phase
- Unhealed fracture of the vertebra and surrounding bone structures
- General cachexia
- Cauda equina syndrome
- Concomitant viral disease
4. Prevention
During therapy, the patient will gain an understanding of the basic anatomy, kinesiology and neurology of the spinal region.
They will learn to independently correct their health problem in the home environment through exercise and minimize the risk of reoccurrence.
Founder Robin McKenzie and his trained therapists place a strong emphasis on prevention. The patient receives helpful hints and tips from the therapist for physiologically performing even the most mundane daily activities.
The patient also gains knowledge about proper ergonomics in the work sphere.

Where can I learn McKenzie movement therapy?
The official website of the McKenzie Institute International, MII for short, lists certified therapists. It makes it easier for patients and healthcare facilities to find therapists.
However, due to legislative laws in some countries, it is not allowed to publicly display this information. Therefore, we recommend contacting the medical facility directly.
Potential patients are advised not to consult health problems and therapy by telephone or e-mail. A personal visit to the facility is necessary, where the patient will be directly instructed and informed about the course of the movement therapy.
In many cases, patients are able to relieve back pain with just a set of basic exercises from the McKenzie Method.
Due to the great interest in self-therapy, Robin McKenzie provides a short book with descriptions of the exercises, photographs and explanations of specific movements.
Currently, a professional publication is available to the public focusing on the treatment of the cervical and lumbar spine, shoulder and knee segments of the human body.
Interesting resources